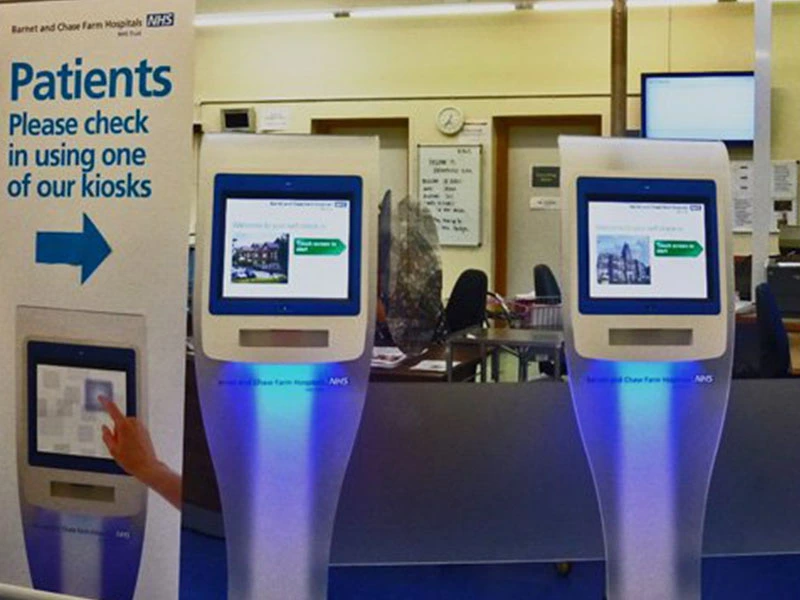
A touchscreen interface is a device with integrated display and input functions. It displays a graphical user interface (GUI) through the screen, and the user performs touch operations directly on the screen with a finger or stylus. The touch screen interface is capable of detecting the user’s touch position and converting it into a corresponding input signal to enable interaction with the interface.

A key component among tablet computers is touch input. This allows the user to navigate easily and type with a virtual keyboard on the screen. The first tablet to do this was the GRiDPad by GRiD Systems Corporation; the tablet featured both a stylus, a pen-like tool to aid with precision in a touchscreen device as well as an on-screen keyboard.
1.Wide range of applications for touch screen technology
Touch screen technology is widely used in the following areas due to its intuitive, convenient and efficient features:
1. Electronic devices
Smartphones: Almost all modern smartphones use touchscreen technology, enabling users to dial numbers, send messages, browse the web, etc. with finger operations.Tablet PCs: such as iPad and Surface, users can use touch operation for reading, drawing, office work and so on.
2. Education
Whiteboards: In classrooms, whiteboards replace traditional blackboards, allowing teachers and students to write, draw and display multimedia content on the screen.Interactive learning devices: such as tablet PCs and touch screen learning terminals, which improve students’ learning interest and interactivity.
3. Medical
Medical equipment: touch screens are used for various medical equipment, such as ultrasound machines and electrocardiographs, simplifying the operation process for healthcare professionals.
Electronic medical records: Doctors can quickly access and record patient information through touch screens, improving work efficiency.
4. Industrial and commercial
Vending machines and self-service terminals: Users operate through the touch screen, such as purchasing tickets and paying bills.
Industrial control: In factories, touchscreens are used to monitor and control production processes, increasing automation.
5. Retail and service industry
Information Query Terminal: In shopping malls, airports and other public places, touch screen terminals provide information query services to facilitate users to obtain the required information.
POS system: In retail industry, touch screen POS system simplifies the cashier and management process.
2. History of touch screen technology
1965-1967: E.A. Johnson develops the capacitive touch screen.
1971: Sam Hurst invents the “touch sensor” and founds Elographics.
1974: Elographics introduces the first true touch panel.
1977: Elographics and Siemens collaborate to develop the first curved glass touch sensor interface.
1983: Hewlett-Packard introduces the HP-150 home computer with infrared touch technology.
1990s: Touch technology is used in mobile phones and PDAs.
2002: Microsoft introduces a tablet version of Windows XP.
2007: Apple introduces the iPhone, which becomes the industry standard for smartphones.
3. What is a touch screen?
A touchscreen is an electronic display that is also an input device. It allows the user to interact with a computer, tablet, smartphone, or other touch-enabled device through gestures and fingertip movements. Touchscreens are pressure sensitive and can be operated with a finger or stylus. This technology eliminates the need for users to use traditional keyboards and mice, thus making the use of the device more intuitive and convenient.
4.Advantages of touch screen technology
1. Friendly to all ages and disabilities
Touch screen technology is user friendly for all ages. Because it is simple and intuitive to use, most people can operate it by simply touching the screen. For people with disabilities, especially those with visual or motor impairments, touch screen technology offers greater ease of use. The touch screen interface can be used with voice prompts and zoom functions, making it easier for people with disabilities to operate.
2. Takes up less space and eliminates the bulkiness of buttons
Touchscreen devices are usually flat, and take up less physical space than traditional devices with a large number of buttons. In addition, the touch screen replaces physical buttons, reducing the complexity and bulkiness of the device, making it lighter and more aesthetically pleasing.
3. Easy to clean
Touchscreen devices have a smooth flat surface that is easy to clean. Compared to traditional keyboards and mice, these devices have fewer crevices and grooves, making them less likely to accumulate dust and dirt. Simply wipe the screen surface gently with a soft cloth to keep the device clean.
4. Durable
Touchscreen devices are usually designed to be sturdy and have a high level of durability. Compared to traditional keyboards and mice, touchscreens do not have as many moving parts and are therefore less susceptible to physical damage. Many touchscreens are also waterproof, dustproof and scratch-resistant, further increasing their durability.
5. Making keyboards and mice redundant
Touchscreen devices can completely replace the keyboard and mouse, making it easier to operate. Users only need to use their fingers directly on the screen for clicking, dragging and input operations, without the need for any other external input devices. This integrated design makes the device more portable and reduces the number of tedious steps in use.
6. Improved accessibility
Touch screen technology greatly improves the accessibility of the device. For those who are not familiar with computer operation or are not good at using the keyboard and mouse, touch screen provides a more direct and natural way of interaction. Users can simply click on icons or options directly on the screen to complete the operation, without having to master complicated steps.
7. Time Savings
Using a touchscreen device can be a significant time saver. Users no longer need to go through multiple steps and complex operations to complete tasks. Tapping directly on the screen options or icons to quickly access and perform the required functions greatly improves productivity and speed of operation.
8. Providing reality-based interaction
Touch screen technology provides a more natural and intuitive interaction where the user can directly interact with the content on the screen. This reality-based interaction makes the user experience richer and more realistic. For example, in a drawing application, the user can draw directly on the screen with a finger or stylus, just as real as drawing on paper.
5. Types of touch screen
1. Capacitive Touch Panel
A capacitive touch screen is a display panel coated with a material that stores an electrical charge. When a finger touches the screen, the charge is attracted at the point of contact, causing a change in the charge near the touch location. Circuitry in the corner of the panel measures these changes and sends the information to the controller for processing. Since capacitive touch panels can only be touched with a finger, they excel in protection against external factors such as dust and water, and have high transparency and clarity.
2. Infrared touch screen
Infrared touch screens work with a matrix of infrared light beams that are emitted by light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and received by phototransistors. When a finger or tool touches the screen, it blocks some of the infrared beams, thus determining the location of the touch. Infrared touchscreens do not require a coating and can achieve high light transmittance, as well as the ability to use a finger or other tool to touch, for a variety of applications.
3. Resistive Touch Panel
Resistive touch screen panel is coated with a thin metal conductive resistive layer, when the screen is touched, the current will change, this change is recorded as a touch event and transmitted to the controller processing. Resistive touchscreens are relatively inexpensive, but their clarity is usually only about 75% and they are susceptible to damage from sharp objects. However, resistive touch screens are not affected by external factors such as dust or water and are suitable for harsh environments.
4. Surface Acoustic Wave Touch Screens
Surface acoustic wave touch panels use ultrasonic waves transmitted through the screen panel. When the panel is touched, a portion of the ultrasonic waves are absorbed, which records the location of the touch and sends that information to the controller for processing. Surface acoustic wave touch screens are one of the most advanced touch screen technologies available, but they are susceptible to dust, water, and other external factors, so they require special attention in terms of cleaning and maintenance.
6. What materials can be used for the touch screen?
Touchscreens can be made from a variety of materials that typically have good conductivity, transparency, and durability. Below are a few common touch screen materials:
1. Glass
Glass is one of the most commonly used materials for touchscreens, especially capacitive touchscreens and surface acoustic wave touchscreens. Glass has excellent transparency and hardness, providing a clear display and good wear resistance. Chemically strengthened or heat-treated glass, such as Corning’s Gorilla Glass, also offers high impact resistance.
2. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
PET is a transparent plastic film commonly used in resistive touchscreens and some capacitive touchscreens. It has good conductivity and flexibility, and is suitable for making touchscreens that need to be bent or folded.PET film is usually coated with conductive materials, such as indium tin oxide (ITO), to improve its conductive properties.
3. Indium Tin Oxide (ITO)
ITO is a transparent conductive oxide that is widely used as an electrode material for various touch screens. It has excellent electrical conductivity and light transmission, enabling highly sensitive touch operations.ITO electrodes are usually coated on glass or plastic substrates by sputtering or other coating techniques.
4. Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is a transparent, durable plastic material sometimes used as a substrate for touch screens. It is lighter and less fragile than glass, making it suitable for application scenarios that require lightweight and impact resistance. However, polycarbonate is not as hard or scratch-resistant as glass, so surface coatings are often required to enhance its durability.
5. Graphene
Graphene is a new 2D material with excellent conductivity and transparency. Although graphene touchscreen technology is still in the development stage, it is expected to be a key material for future high-performance touchscreens. Graphene has excellent flexibility and strength, making it suitable for bendable and foldable touchscreen devices.
6. Metal Mesh
Metal mesh touchscreens use very fine metal wires (usually copper or silver) woven into a grid structure, replacing the traditional transparent conductive film. Metal Mesh Touch Panels have high conductivity and light transmission, and are particularly suitable for large-size touch panels and ultra-high resolution displays.
7. What are the touch screen devices?
Touch screen devices are electronic devices that use touch screen technology for human-computer interaction and are widely used in various fields. The following are some common touch screen devices and their applications:
1. Smartphone
Smartphones are one of the most common touchscreen devices. Almost all modern smartphones are equipped with capacitive touchscreens that enable users to operate the device through finger swiping, tapping, zooming, and other gestures. The touchscreen technology of smartphones not only enhances the user experience, but also provides rich interaction methods for application development.
2. Tablet PC
Tablet PCs are also a widely used touchscreen device, usually with a large screen, suitable for browsing the web, watching videos, drawing and other multimedia operations. Similar to smartphones, tablets usually use capacitive touchscreen technology, but some devices also use resistive or other types of touchscreens.
3. Self-service terminals
Self-service terminals (e.g., ATMs, self-checkout machines, self-service ticket machines, etc.) use touchscreen technology to provide convenient self-service. These devices are usually installed in public places, allowing users to perform various operations through the touch screen, such as inquiring information, handling business, purchasing goods, etc.
4. In-vehicle infotainment system
The in-vehicle infotainment systems of modern cars are usually equipped with touchscreens that provide navigation, music playback, telephone communication, vehicle settings and other functions. The touchscreen interface simplifies the driver’s operation and makes it easier to access and control various functions.
5. Smart Home Devices
Many smart home devices (e.g., smart speakers, smart thermostats, smart refrigerators, etc.) are also equipped with touchscreens. Users can control these devices directly through the touchscreen interface for home automation and remote management.
6. Industrial Control Devices
In the industrial field, touch screen devices are used to monitor and control production processes. Industrial touchscreens are usually durable, waterproof and dustproof, and can work properly in harsh environments. These devices are widely used in factory automation, intelligent manufacturing, energy management and other fields.
7. Medical equipment
The application of touch screen technology in medical equipment is also becoming more and more common. For example, ultrasonic diagnostic instruments, electronic medical record systems, and surgical assistive devices are equipped with touch screen interfaces to facilitate operation and recording by medical personnel.
8. Game equipment
The application of touch screen technology in gaming devices greatly enriches the gaming experience. Mobile games on smart phones and tablet PCs, touch-screen all-in-one gaming devices, etc., all use touch-screen technology to provide intuitive operation and interactive experience.
8. Multi-touch gestures
Multi-touch gesture is an interactive way of using multiple fingers to operate on a touch screen, which can achieve more functions and more complex operations than single-touch. The following are some common multi-touch gestures and their applications:
1. Drag
Operation method: Press and hold an object on the screen with one finger, and then move the finger.
Application scenarios: moving icons, dragging files, adjusting the position of the slider and so on.
2. Zoom (Pinch-to-Zoom)
Operation method: touch the screen with two fingers at the same time, then separate the fingers (zoom in) or close them (zoom out).
Application Scenario: Zoom in or out in photo viewing application, zoom in or out in map application, etc.
3. Rotate
How to use: Touch the screen with two fingers, then rotate your fingers.
Scenarios: Rotate a picture or object, such as adjusting the angle of a photo in photo editing software.
4. Tap
How to use: Use one finger to touch the screen once quickly.
Scenarios: open an application, select an item, confirm an operation, and so on.
5. Double Tap
Operation method: Use one finger to quickly touch the screen twice.
Scenarios: zoom in or out of the web page or picture, select text, etc.
6. Long Press
How to use: Press and hold the screen with one finger for a certain period of time.
Application Scenario: Call out the context menu, start dragging mode, select multiple items, and so on.
7. Slide (Swipe)
How to use: Use one finger to quickly slide on the screen.
Scenarios: turning pages, switching pictures, opening the notification bar or shortcut settings, and so on.
8. Three-Finger Swipe (Three-Finger Swipe)
How to use: Use three fingers to slide on the screen at the same time.
Application Scenario: In some applications can be used to switch tasks, adjust the page layout.
9. Four-Finger Pinch (Four-Finger Pinch)
Operation method: Pinch on the screen with four fingers.
Application Scenario: In some operating systems, it can be used to return to the home screen or call up the task manager.
9. What’s in the touchscreen?
1. Glass Panel
Function: The glass panel is the outer layer of the touch screen and serves to protect the internal components while providing a smooth touch surface.
2. Touch Sensor
Type:
Capacitive Sensor: Uses changes in electric field to detect touch.
Resistive sensors: work by detecting changes in pressure between two layers of conductive material.
Infrared Sensor: Uses an infrared beam to detect touch points.
Acoustic Sensor: Uses the propagation of sound waves across the surface of the screen to detect touch.
Function: The touch sensor is responsible for detecting the user’s touch operations and converting these operations into electrical signals.
3. Controller
Function: The controller is a microprocessor that processes signals from the touch sensor. It converts these signals into commands that the device can understand and then passes them on to the operating system.
4. Display Type
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD): displays images and text by controlling the liquid crystal pixels.
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) Display: Displays images by emitting light from organic materials with higher contrast and lower energy consumption.
Function: The display is responsible for displaying the user interface and content, and is the main part of the user’s visual interaction with the device.
5. Protective Layer
Function: The protective layer is a transparent covering, usually tempered glass or plastic, that protects the touchscreen from scratches, bumps, and other physical damage.
6. Backlight Unit
Function: In an LCD touchscreen, the backlight unit provides the light source that enables the display to show images and text. The backlight usually consists of LEDs.
7. Shielding layer
Function: The shielding layer is used to prevent electromagnetic interference and ensure the normal operation of the touch screen and the accurate transmission of signals.
8. Connection cable
Function: The connecting cable connects the touch screen assembly to the main board of the device and transmits electrical signals and data.
9. Coating Type:
Anti-fingerprint coating: reduces fingerprint residue on the screen and makes the screen easier to clean.
Anti-Reflective Coating: Reduces screen reflections and improves visibility.
Function: These coatings enhance the user experience and durability of the touchscreen.
10. Stylus (optional)
Function: Some touchscreen devices are equipped with a stylus for more precise operation and drawing.
10. Touch screen monitors
A touchscreen monitor is a device that can input and receive information via a touchscreen, typically used in laptops, tablets, and other touch-enabled devices. It combines both display and input functions, enabling users to interact with the device more intuitively and easily.
Key Features
Single peripheral:
Touchscreen monitors integrate display and touch input functions, allowing users to operate without an additional keyboard or mouse.
Provides a cleaner user experience and reduces reliance on external input devices.
Intuitive user experience:
Users can operate directly on the screen, controlling the device through gestures such as tapping, swiping, and dragging with a finger or stylus. This intuitive operation makes the device more convenient to use, low learning cost, suitable for users of all ages.
Multiple application scenarios:
Touch screen monitors are widely used in education, business, medical, industrial and other fields. For example, in the field of education, touch-screen monitors can be used for interactive teaching; in the commercial field, touch-screen monitors can be used to display products, customer service; in the medical field, touch-screen monitors can be used to view and enter patient information.
Its versatility makes it useful in a variety of environments.
Efficient data entry:
Users can enter data directly on the screen, eliminating the need to use a keyboard and mouse, which improves work efficiency.
The touchscreen monitor can also be equipped with a virtual keyboard for easy text input.
Cleaning and Maintenance:
Touch screen monitors usually have a smooth glass or plastic surface that is easy to clean and maintain.
By reducing the use of external devices such as keyboards and mice, the accumulation of dust and dirt is reduced, keeping the device tidy.
Improved accessibility:
For users with special needs, such as the elderly or the physically challenged, touch screen monitors offer a more convenient way to operate.
Users can complete complex operations with simple touches and gestures, improving the usability and ease of use of the device.
11. The future of touch screen technology
Touch technology may evolve to touchless technology
One of the trends in touch technology is the shift to touchless technology. Touchless technology allows users to interact without actually touching the screen, reducing the need for physical contact. This technology offers significant advantages in terms of hygiene and sanitisation, particularly in public places and healthcare environments, reducing the risk of spreading viruses and bacteria. Through gesture recognition and near-field communication technologies such as infrared, ultrasound and cameras, touchless technologies are able to accurately recognise the user’s gestures and intentions to enable touchscreen functionality.
Explore Predictive Touch Technology
Predictive touch technology is an innovative technology that uses sensor data and artificial intelligence to predict user intent. By analysing the user’s gestures and movement trajectory, Predictive Touch can identify in advance what the user wants to touch and respond before the user actually touches the screen. This technology not only improves the accuracy and speed of touch operations, but also reduces the user’s contact time with the screen, further reducing the risk of wear and tear and damage to touch devices. Predictive touch technology is currently being tested in the laboratory and is expected to be applied to a variety of touch devices in the near future.
Development of Touch Walls for Laboratories and Hospitals
Touch walls are an extended application of touch screen technology on large display devices, mainly used in specialised environments such as laboratories and hospitals. These touch walls can be used as interactive whiteboards, data presentation platforms and operation control centres to help researchers and healthcare professionals process and present information more efficiently. For example, in laboratories, touch walls can display experimental data and results to support multi-user collaboration and real-time data analysis; in hospitals, touch walls can display patient information and medical images to help healthcare professionals with diagnosis and treatment. With the continuous progress of touch technology, touch walls will be increasingly used in various professional environments to enhance work efficiency and information processing capabilities.
Extended Multi-Touch Gesture Support
Multi-touch gesture is an important part of touch screen technology, which allows users to operate with multiple fingers at the same time, thus achieving more interactive functions. In the future, with the continuous development of hardware and software technology, multi-touch gesture support will be further expanded, enabling touch devices to recognise and respond to more complex gestures. For example, users can zoom, rotate and drag objects through different combinations and movement trajectories of their fingers, or invoke shortcut operations and applications through specific gestures. This will greatly enhance the flexibility and experience of touch devices, making touch operations more intuitive and efficient.

Penny
Web Content Writer
4 years of experience
This article is edited by Penny, the website content writer of COMPT, who has 4 years working experience in the industrial PCs industry and often discusses with colleagues in R&D, marketing and production departments about the professional knowledge and application of industrial controllers, and has a deep understanding of the industry and products.
Please feel free to contact me to discuss more about industrial controllers. sales@gdcompt.com