What is VGA?
-
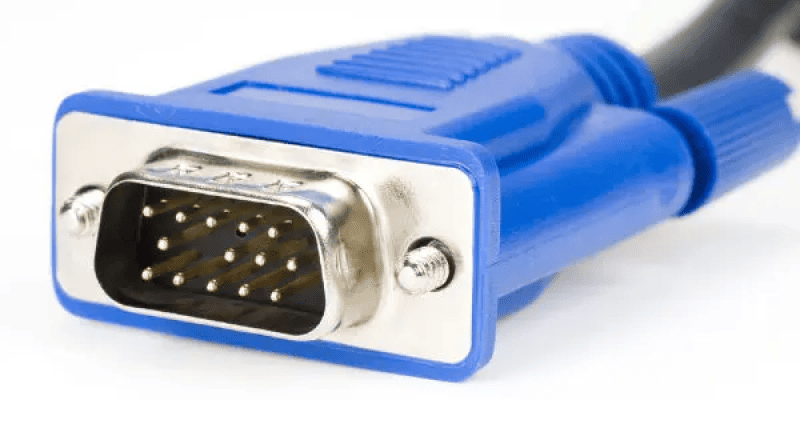
VGA Interface Definition: VGA (Video Graphics Array), also known as the D-Sub interface, is an analog video transmission standard introduced by IBM in 1987. It became one of the most widely used interface types on graphics cards, primarily for connecting CRT monitors.
-
Transmission Method: The VGA interface transmits analog signals, including red, green, and blue (RGB) color signals, along with horizontal and vertical synchronization signals. When connecting to digital display devices such as LCDs or DLPs, VGA signals require additional analog-to-digital (A/D) converters to be transformed into digital signals.
-
Resolution and Compatibility: The maximum output resolution of the VGA interface is 1080p (2 million pixels), making it suitable for most legacy devices. As technology has advanced, VGA has gradually been replaced by more modern interfaces like DVI, HDMI, and DisplayPort. However, it remains useful for connecting older equipment that still relies on VGA.
What is an HDMI Interface?
-
Definition: HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is a digital video and audio interface standard established by the HDMI Forum. It enables the simultaneous transmission of high-quality video and audio signals over a single cable, simplifying connections between devices such as TVs, monitors, and computers.
-
Transmission Method: HDMI transmits digital signals, offering higher resistance to interference and longer transmission distances compared to analog interfaces. It supports high-definition resolutions up to 8K, making it suitable for modern high-resolution displays and televisions.
-
Compatibility and Plug-and-Play: HDMI devices support EDID (Extended Display Identification Data) and DDC2B (Display Data Channel 2B) protocols, enabling plug-and-play functionality. This allows devices to automatically select the most appropriate video and audio formats for optimal performance.
Key Differences Between HDMI and VGA
Video Quality: HDMI supports higher resolutions and faster refresh rates, catering to modern high-definition and ultra-high-definition video requirements. VGA, being an older analog standard, is limited to lower resolutions like 1080p.
Interference Resistance: HDMI’s digital signal transmission provides superior resistance to electromagnetic interference, especially beneficial for large displays, high resolutions, and long-distance connections.
Transmission Distance: While VGA’s maximum transmission distance is approximately 15 meters, HDMI can extend up to 300 meters using appropriate extenders, highlighting HDMI’s advantage in long-distance signal transmission.
Applications of VGA in HDMI
1. Device Compatibility
1.1 Connecting Older Devices to New Displays
Some older devices, such as legacy desktop computers, are equipped only with VGA output. When users wish to connect these devices to modern displays or televisions that feature HDMI inputs, a VGA in HDMI converter becomes essential. For instance, an office computer manufactured around 2010 may only support VGA output, while the office has upgraded to high-definition large-screen displays with HDMI interfaces for presenting documents or video materials.
1.2 Signal Conversion for Specialized Equipment
Certain professional equipment, like early video editing workstations or medical imaging devices, output signals in VGA format. To display images from these devices on modern screens equipped with HDMI inputs, a VGA in HDMI conversion is necessary.
2. Signal Transmission and Functional Requirements
2.1 Temporary Solutions for High-Definition Display Needs
In temporary presentation scenarios, if only a VGA-output video source (such as a laptop) is available and the display device (like a projector or large screen) has an HDMI input, and the image quality requirements are not stringent (e.g., simple document presentations or small video playback), a VGA in HDMI converter can facilitate the connection.
2.2 Expanding Display Capabilities
In multi-screen setups, such as monitoring centers, some older surveillance cameras may output VGA signals, while the monitoring room’s video wall comprises multiple HDMI-input displays. Utilizing VGA in HDMI converters allows these VGA signal sources to be integrated into the overall monitoring display system.
3. Cost and Convenience Considerations
3.1 Low-Cost Display Connection Upgrades
Instead of replacing entire devices to match interface types, using a VGA in HDMI converter is a more economical approach. For example, individual users who prefer not to invest heavily in upgrading computer hardware to obtain HDMI outputs can simply purchase a converter to connect their existing VGA-output computers to new HDMI televisions for watching online videos or gaming.
3.2 Portable Conversion Needs
In mobile office settings or temporary exhibition scenarios, portable VGA in HDMI converters enable convenient connections between devices with different interfaces. For instance, sales personnel visiting clients may need to connect the company’s VGA-output promotional video equipment to the client’s HDMI-input large-screen television for presentations.
How to Connect a VGA Device to an HDMI Interface?
1. Using a VGA to HDMI Converter
This method is suitable when your source device has a VGA output and your display device has an HDMI input.
Steps:
-
Purchase a VGA to HDMI converter.
-
Connect the VGA output of your device to the VGA input of the converter.
-
Connect one end of an HDMI cable to the HDMI output of the converter and the other end to the HDMI input of your display device (such as a TV or monitor).
-
If audio transmission is needed, use a 3.5mm audio cable to connect the audio output of your VGA device to the audio input of the converter.
-
Ensure the converter is powered appropriately, either through a USB connection or an external power source, as some converters require power to function correctly.
-
ourtechroom.com
2. Using an HDMI to VGA Converter
This method is applicable when your source device has an HDMI output and your display device has a VGA input.
Steps:
-
Purchase an HDMI to VGA converter.
-
Connect the HDMI output of your device to the HDMI input of the converter.
-
Connect one end of a VGA cable to the VGA output of the converter and the other end to the VGA input of your display device.
-
Note that this setup is not the same as “VGA in HDMI” and is used for the reverse connection.
3. Direct HDMI Connection (Applicable to Certain Computers or Monitors)
If your computer or monitor is equipped with both VGA and HDMI interfaces, you might be able to connect them directly using an HDMI cable.
Considerations:
This method typically applies to newer devices that support both interfaces.
Older devices may not support signal conversion between VGA and HDMI through a direct cable connection.
How to choose the right VGA in HDMI converter?
1. Understand Your Device’s Interface Types
First, identify the output and input interfaces of your devices. If your source device (e.g., a computer) has a VGA output and your display device (e.g., a monitor or TV) has an HDMI input, you’ll need a VGA in HDMI converter. Conversely, if your source device has an HDMI output and your display has a VGA input, an HDMI to VGA converter is required. Ensuring the correct converter type is crucial for proper signal transmission.
2. Choose a Converter with Quality and Brand Reliability
Select a converter that matches your usage needs. For occasional use, standard models may suffice. However, for high-quality video output, consider converters from reputable brands known for performance and durability. Features to look for include support for resolutions up to 1080p, audio transmission capabilities, and robust build quality. Brands like Cable Matters and FOINNEX offer converters with these specifications .
MakeUseOf
3. Ensure Compatibility and Quality
Opt for converters from reputable brands and sellers to guarantee quality and compatibility. High-quality converters typically include advanced chips for stable signal conversion, support for audio transmission, and are compatible with various operating systems. Avoid low-quality converters that may use inferior materials or chips, as they can lead to poor video signal quality or device incompatibility.
4. Usage Tips for Converters
-
Connect the converter to the appropriate VGA or HDMI port on your device.
-
Use the corresponding cable to connect the converter to your display device.
-
Ensure all connections are secure.
-
Adjust your device’s display settings to select the correct input source.
-
By following these guidelines, you can effectively choose and use a VGA in HDMI converter that meets your specific requirements.
What about vga in hdmi no signal?
1. Verify Cable and Connection Integrity
Ensure that the VGA to HDMI converter is securely connected to both the VGA output of your source device and the HDMI input of your display.
Inspect the cables for any visible damage or wear.
If possible, test with a different VGA to HDMI converter to rule out a faulty hdmi in vga out adapter.
2. Confirm the Correct Input Source on the Display
Access your display’s input/source settings and ensure it is set to the HDMI port connected to the converter.
Some displays may not automatically detect the active input source, requiring manual selection.
3. Adjust Computer Display Settings
-
Update your computer’s graphics drivers to the latest version to ensure compatibility.
-
Set the display resolution to a value supported by your monitor (e.g., 1024×768 or 1280×720).
-
High resolutions may not be supported through certain converters, leading to a “no signal” display.
4. Check Display Settings
Some monitors have an “auto-detect” feature for input sources.
If available, enable this feature or manually select the correct HDMI input.
5. Assess Device Compatibility
Older monitors may not support certain resolutions or refresh rates output by newer graphics cards.
Ensure that both your source device and display are compatible with the converter being used.
6. Restart Devices
-
Power off both your computer and monitor.
-
Disconnect the VGA to HDMI converter and all cables.
-
Reconnect everything securely and power on the devices.
-
A fresh start can sometimes resolve connectivity issues.
What to Do If Your VGA to HDMI Connection Is Flickering?
1. Low-Quality Converter
Using a substandard VGA to HDMI converter can lead to signal instability and flickering.
Recommendation: Opt for converters from reputable brands that meet industry standards. High-quality converters are more likely to provide stable signal transmission and reduce flickering issues.
2. Unstable Signal Transmission
Poor-quality or damaged cables can cause intermittent signal transmission, resulting in flickering.
Recommendation: Use high-quality VGA and HDMI cables to ensure stable connections. Avoid using excessively long cables, as signal degradation can occur over extended distances.
3. Resolution and Refresh Rate Mismatch
An incompatible resolution or refresh rate between your computer and monitor can cause display issues, including flickering.
Recommendation: Adjust your computer’s display settings to match the native resolution and refresh rate of your monitor. Common refresh rates are 60Hz or 75Hz, but it’s essential to use settings supported by both devices.
4. Outdated Graphics Drivers
Outdated or corrupted graphics drivers can lead to various display problems, including flickering.
Recommendation: Update your graphics drivers to the latest version provided by your hardware manufacturer. This can often resolve compatibility issues and improve display performance.
5. Electromagnetic Interference
Devices emitting electromagnetic interference, such as routers or speakers, can disrupt signal transmission and cause flickering.
Recommendation: Ensure that your VGA and HDMI cables are not running parallel to power cables or placed near devices that emit electromagnetic interference. Maintaining a distance of at least one meter between such devices and your display setup can help minimize interference.
6. Hardware Issues
If the above solutions do not resolve the flickering, there may be underlying hardware problems with your graphics card, monitor, or the converter itself.
Recommendation: Test your setup with different devices to isolate the issue. If necessary, consult a professional technician to diagnose and address hardware faults.
By systematically addressing these potential causes, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve VGA to HDMI flickering issues.
Customized VGA and HDMI Interface Solutions by COMPT
COMPT‘s Panel PCs and Industrial Monitors offer customizable solutions tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you need multiple VGA inputs, several HDMI ports, or a specific combination of both, we can design and manufacture industrial panel PCs to your exact specifications. This customization eliminates the need for additional converters or hdmi in vga adapter, simplifying your system integration and enhancing stability and efficiency. Feel free to contact us to discuss your specific needs, and we will provide the most suitable customized solution for your application.

Penny
Web Content Writer
4 years of experience
This article is edited by Penny, the website content writer of COMPT, who has 4 years working experience in the industrial PCs industry and often discusses with colleagues in R&D, marketing and production departments about the professional knowledge and application of industrial controllers, and has a deep understanding of the industry and products.
Please feel free to contact me to discuss more about industrial controllers. sales@gdcompt.com